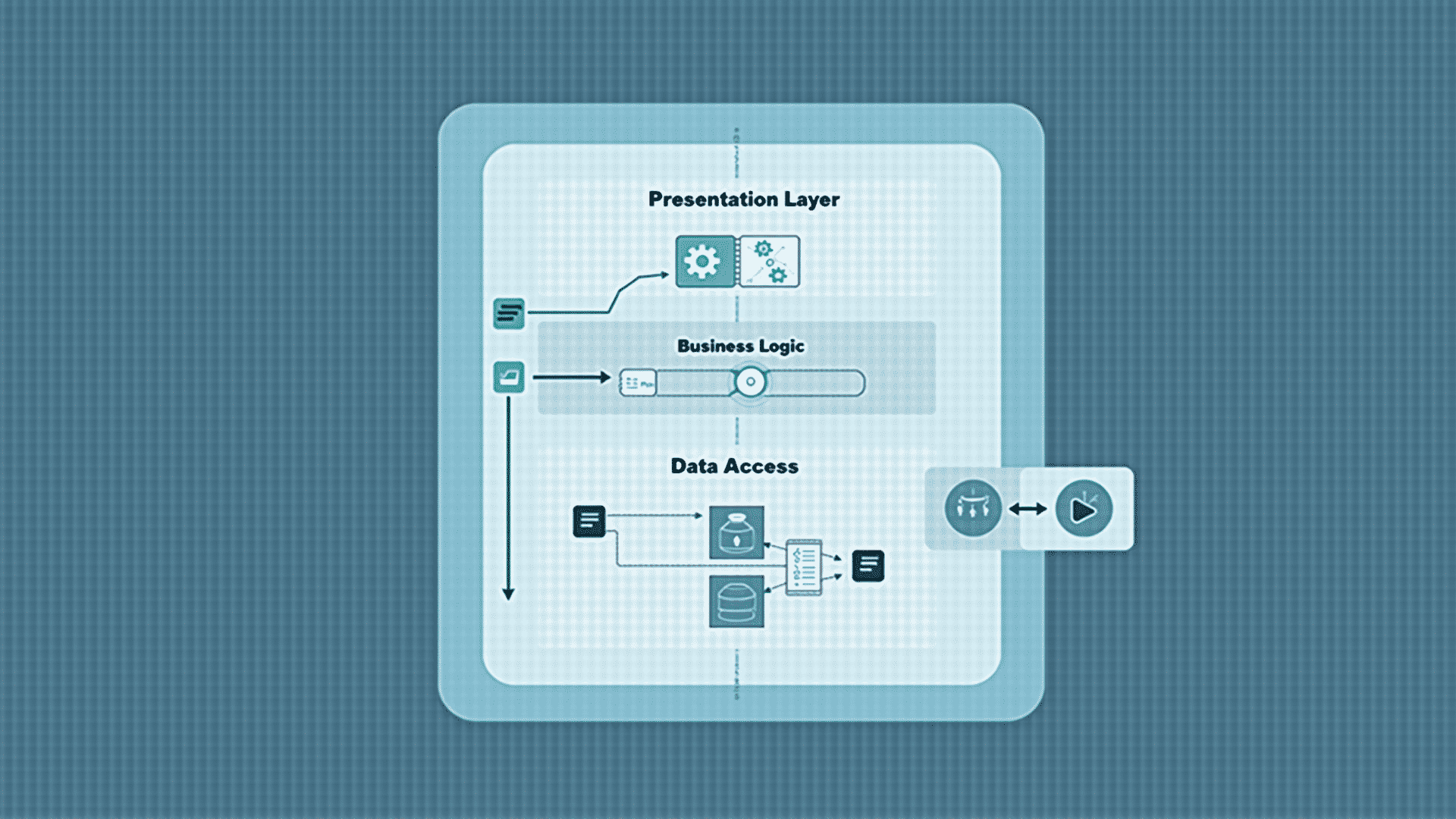
Understanding the foundational structure of application architecture is crucial for developing efficient and robust digital solutions. This structure encompasses numerous key components and follows best practices to ensure that the final product is scalable, maintainable, and adaptable. Here's an overview of the essentials that define solid application architecture.
At the core of any application lies the architectural pattern chosen to guide its design and development. Various patterns are available, each suitable for different types of projects. Commonly used patterns include Model-View-Controller (MVC), Model-View-ViewModel (MVVM), and Microservices, among others. Each pattern provides a structured approach to separate concerns in the application, allowing for more focused development efforts and efficient testing.
A critical component of an application’s architecture is its data management strategy. This involves determining how data is stored, accessed, and manipulated. Choosing the appropriate database architecture—whether relational, non-relational, or in-memory—depends on the application's specific needs and expected data workload. Effective database design ensures that data operations are performed efficiently and that the application can scale as required.
Another essential aspect is the user interface (UI) and user experience (UX) design. The UI represents how the application interacts with users, and a well-designed interface contributes significantly to the overall user experience. Ensuring that the UI is intuitive and responsive is key to user retention and satisfaction. This often involves iterative testing and refinement based on user feedback.
Security is another pillar of strong application architecture. Protecting both the application and its users' data must be prioritized throughout development. Implementing secure authentication mechanisms, data encryption, and regular security audits are practices that safeguard against vulnerabilities and unauthorized access.
Additionally, considering the performance optimization aspect from early development stages helps in creating applications that are responsive and efficient under load. Techniques such as caching, load balancing, and asynchronous processing are vital for maintaining speed and reliability.
Testing and continuous integration also play influential roles in sustainable application development. Frequent code testing ensures that new changes do not introduce errors or degrade performance, while continuous integration allows for seamless merging of new features and improvements into the existing codebase.
Lastly, maintaining thorough documentation throughout the lifecycle of the application is indispensable. This practice aids in onboarding new team members, simplifies troubleshooting, and serves as a reference for future enhancements.
By incorporating these elements into the design and development process, one can ensure the creation of robust, adaptable, and successful digital solutions. Focusing on these foundational aspects lays the groundwork for applications that not only meet current requirements but also evolve seamlessly with technological advancements and user needs.